Maternal mortality rates in the United States continue to alarm public health officials, revealing stark disparities in pregnancy-related deaths across various demographic groups. For a nation that leads its high-income peers in maternal health crises, the fact that over 80% of these fatalities are preventable underscores a pressing need for reform. Recent studies highlight alarming trends, showing an increase in maternal mortality rates during the past few years, particularly among American Indian and Black women who face significant healthcare inequities. Beyond just statistics, the rise in these rates calls for comprehensive improvements in prenatal care and postpartum support systems. Addressing preventable maternal mortality requires a concerted effort to eliminate racial disparities within maternal health services while ensuring equitable access to quality care for all women.
The issue of pregnancy-related fatalities in the U.S. reflects a deeper crisis within maternal healthcare, where alarming statistics and inequities converge. This ongoing struggle includes issues such as avoidable maternal deaths and the profound impacts of systemic bias on various racial groups. Recent research reveals the necessity for enhanced support during the perinatal period, emphasizing the importance of addressing postpartum care improvements to better safeguard maternal well-being. As the nation grapples with growing healthcare disparities, the urgency to reform existing policies and practices becomes increasingly crucial. By understanding and confronting these challenges, healthcare providers can work toward eliminating preventable maternal mortality and fostering a healthier future for all mothers.
Understanding Maternal Mortality Rates in the U.S.
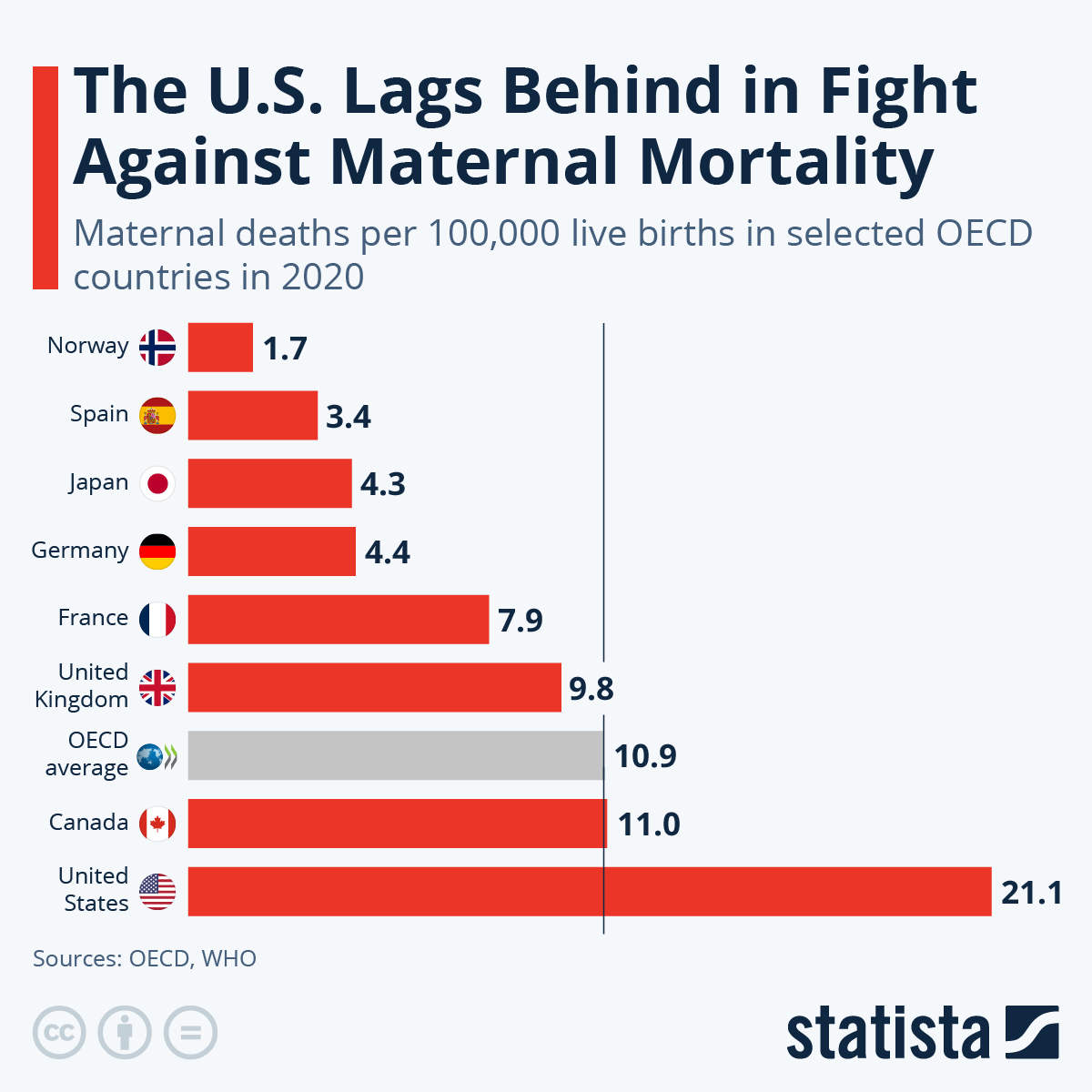
Maternal mortality rates in the U.S. have become a pressing public health issue, as they continue to surpass those of other high-income countries. Between 2018 and 2022, there was a notable increase in the number of pregnancy-related deaths, demonstrating systemic failures in maternal healthcare. More than 80 percent of these deaths are deemed preventable, which raises urgent questions about the effectiveness of existing healthcare policies and practices. Addressing these high mortality rates demands a multifaceted approach that encompasses proactive care during pregnancy and targeted interventions during the postpartum period.
The alarming rise in maternal mortality rates can mainly be attributed to chronic health conditions such as cardiovascular diseases, which have shifted from being a secondary concern to the leading cause of pregnancy-related deaths. Furthermore, significant disparities exist based on race and ethnicity, with American Indian and Alaska Native women facing disproportionately higher mortality rates than their white counterparts. This troubling trend emphasizes the need for comprehensive maternal health reforms that consider social determinants of health and ensure equitable access to quality healthcare services.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main causes of pregnancy-related deaths in the U.S. contributing to high maternal mortality rates?
The main causes of pregnancy-related deaths contributing to the high maternal mortality rates in the U.S. include cardiovascular disease, hemorrhage, and severe hypertension conditions such as pre-eclampsia. These issues are often exacerbated by healthcare inequities and lack of access to quality prenatal and postpartum care.
How do racial disparities affect maternal mortality rates in the U.S.?
Racial disparities significantly affect maternal mortality rates in the U.S., with American Indian and Alaska Native women experiencing the highest rates (106.3 deaths per 100,000 live births). Non-Hispanic Black women also face substantial rates (76.9 deaths per 100,000 live births), showcasing the need for targeted interventions to address these preventable maternal mortality issues.
What role does postpartum care play in preventing maternal mortality rates?
Postpartum care is crucial in preventing maternal mortality rates, as nearly a third of pregnancy-related deaths occur after 42 days postpartum. Enhancing postpartum care can address ongoing health issues and reduce risks associated with cardiovascular diseases and other chronic conditions that may arise during this critical period.
Why is it vital to address healthcare inequities in relation to maternal mortality rates?
Addressing healthcare inequities is vital to reducing maternal mortality rates because disparities in access to care disproportionately affect marginalized groups. Improving access to comprehensive maternal health services can help ensure all women receive the necessary care during pregnancy and postpartum, leading to better health outcomes.
What recommendations do researchers suggest for reducing preventable maternal mortality rates?
Researchers recommend increasing investment in quality maternal health care, addressing state-level policy differences, and enhancing public health infrastructures to track and prevent pregnancy-related deaths. These measures are essential to improve maternal health outcomes and reduce preventable maternal mortality rates across diverse populations.
How does the U.S. maternal mortality rate compare to other high-income countries?
The U.S. maternal mortality rate is the highest among high-income countries, with over 80% of these deaths being preventable. Factors such as access to quality prenatal care and healthcare inequities contribute to this alarming statistic.
What have studies revealed about the trends in maternal mortality rates over recent years?
Studies have revealed that maternal mortality rates in the U.S. have continued to rise from 2018 to 2022, with significant increases noted during 2021, likely due to the COVID-19 pandemic. These rising trends highlight the urgent need for improved maternity care and postpartum support.
What can be done to ensure better data collection on maternal mortality rates?
To ensure better data collection on maternal mortality rates, it is crucial to maintain and enhance systems for tracking pregnancy-related deaths consistently. The implementation of pregnancy checkboxes on death certificates is a positive step, but further investment in data collection processes and funding for research is necessary to fully understand and address these issues.
What implications do late maternal deaths have on the understanding of maternal health?
Late maternal deaths, which occur between 42 days and one year post-pregnancy, highlight the importance of a continuum of care beyond the immediate postpartum period. Recognizing these deaths underscores the need for comprehensive maternal health policies that extend support and care throughout the entire first year after childbirth.
How can state-level variations in maternal mortality rates be addressed?
Addressing state-level variations in maternal mortality rates requires analyzing the underlying causes of disparities in healthcare access and quality across different states. Policymakers must focus on implementing effective maternal health programs and practices observed in states with lower mortality rates to improve outcomes nationwide.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Rising Rates of Maternal Mortality | Over 80% of U.S. pregnancy-related deaths are preventable; rates rose from 25.3 to 32.6 deaths per 100,000 live births from 2018 to 2022. |
| Disparities in Mortality Rates | Significant disparities across racial and ethnic groups, with American Indian and Alaska Native women having the highest rates at 106.3 deaths per 100,000 live births. |
| Impact of COVID-19 | The sharpest increase occurred in 2021, reflecting the pandemic’s effects, with ongoing high rates subsequent to 2020. |
| Leading Causes of Maternal Death | Cardiovascular disease is now the leading cause, contributing to over 20% of pregnancy-related deaths. |
| Need for Improved Healthcare Systems | Advocacy for better prenatal care and postpartum support, addressing systemic biases, and focusing on state policy disparities are crucial. |
| Late Maternal Deaths | Nearly one third of maternal deaths occur between 42 days and one year postpartum, highlighting gaps in care during this period. |
Summary
Maternal mortality rates in the United States continue to rise, highlighting a pressing public health crisis. Despite advancements in medical care, over 80% of these deaths remain preventable, underscoring the urgent need for comprehensive healthcare reforms. Key issues such as racial disparities, inadequate postpartum care, and the impacts of chronic conditions significantly contribute to these troubling trends. As we move forward, it is vital to focus on policy changes, increase investments in public health infrastructure, and improve access to quality maternal healthcare to address the alarming rise in maternal mortality rates.