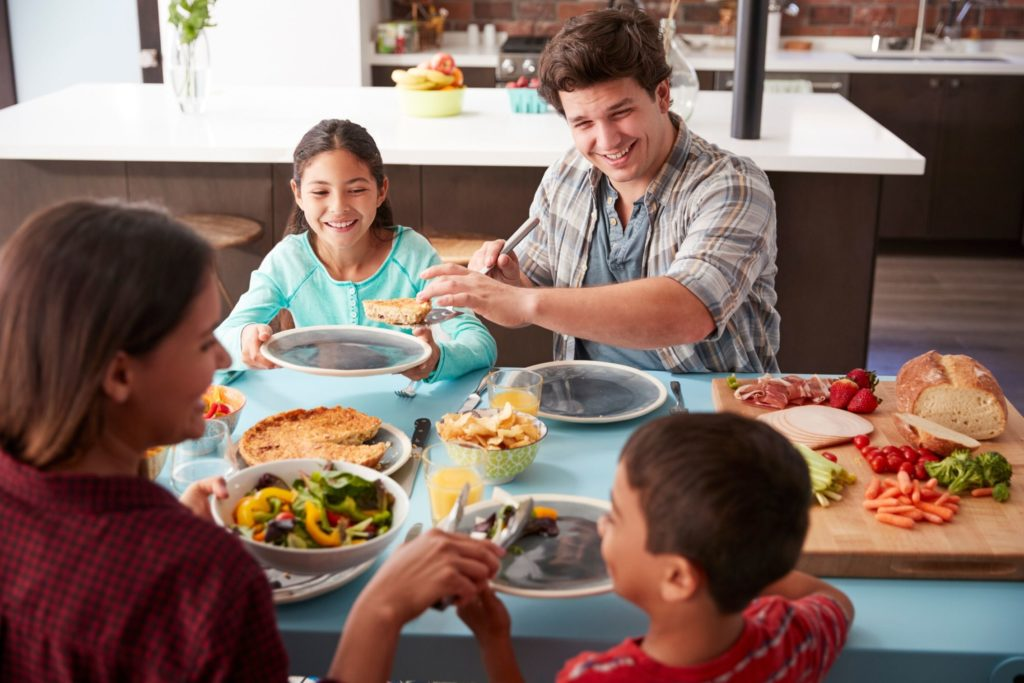
Shared meals and happiness are deeply intertwined, with evidence suggesting that dining with others can be a prolific source of joy and contentment. Research indicates that individuals who frequently enjoy meals in company experience higher levels of life satisfaction and express more positive emotions. According to a study featured in the World Happiness Report, the act of meal sharing serves as a significant happiness indicator, rivaling even financial status in its correlation with social well-being. However, alarming trends reported by the American Time Use Survey reveal that many Americans are eating alone, with a staggering one in four individuals dining solo daily. This increase in solitary meals only underscores the importance of understanding the meal sharing benefits for enhancing communal harmony and emotional health.
The connection between communal dining and emotional fulfillment opens up a fascinating dialogue on social interactions and well-being. Engaging in collective meals is not merely a cultural tradition; it emits positive feelings that can significantly uplift one’s mood. Various studies reinforce the notion that eating together enhances one’s happiness indicators, playing a crucial role in the landscape of social health. As the data from the American Time Use Survey illustrates a growing trend of solitary dining, it becomes increasingly vital to explore the implications of meal sharing on our mental states and relationships. Ultimately, fostering an environment where individuals can reconnect over meals may pave the way for enhanced happiness and stronger community bonds.
Shared Meals: A Reflection of Happiness
The act of sharing meals has long been associated with cultural traditions and community bonding, and recent research now substantiates this age-old belief by linking dining with others to improved happiness. According to findings from the World Happiness Report, individuals who regularly share meals demonstrate higher life satisfaction and express more positive emotions. This correlation shines a light on dining as a powerful social activity that not only fosters connection but also serves as a reliable indicator of well-being, comparable to traditional measures like income or employment status.
However, the increase in solitary dining observed in the American Time Use Survey raises significant concern. With 1 in 4 Americans reporting eating all their meals alone in recent years, researchers are prompted to question the impact of such social isolation on emotional health. The compelling argument made by public policy experts is that enhancing social participation, through shared meals, could serve as a key intervention in improving overall happiness across diverse communities.
The Benefits of Meal Sharing for Social Well-Being
Sharing meals extends beyond mere consumption of food; it embodies a practice that enriches social bonds and enhances social well-being. When individuals gather around a table, they engage in not just the sharing of dishes, but also the exchange of ideas, experiences, and laughter. This dynamic interaction contributes to the development of stronger social networks and an increased sense of community belonging. Hence, meal sharing can act as a catalyst for fostering relationships that support mental health and happiness.
Moreover, the scientific analysis surrounding happiness indicators illustrates the potential benefits of dining together. In contrast to other metrics like financial income—which can fluctuate and are often difficult to assess—measuring the frequency of shared meals offers a more tangible and straightforward metric of social engagement. By prioritizing meal sharing, societies could reap the dual benefits of enhancing individual well-being and strengthening community ties.
Understanding the Connection: Meals and Happiness Indicators
The empirical evidence linking shared meals with happiness suggests that the frequency of dining together has far-reaching implications for measuring happiness indicators. The study, which emphasizes this correlation, opens a dialogue about how social interactions, facilitated through meal sharing, could be a more significant predictor of happiness than monetary factors. This insight calls for a reevaluation of how happiness is quantified and understood in societal contexts.
Additionally, this connection raises questions about the nature of happiness itself. Are happier individuals more likely to seek out shared meals, or does engaging in meal sharing actively foster a greater sense of joy? This dialogue invites further research into how social interactions during meals can be leveraged as a strategic approach to enhancing mental well-being and quality of life across populations.
Exploring the Impact of Solitary Dining
The American Time Use Survey findings indicate a stark trend: a significant increase in solitary dining among Americans. This shift raises critical questions about the implications of social isolation on overall happiness and well-being. Eating alone can result in a plethora of adverse effects on mental health, as the absence of social interaction during meals deprives individuals of the emotional support and joy that arise from communal dining experiences.
Furthermore, as the rates of individuals dining alone continue to rise, it becomes imperative for policymakers to address this issue. By encouraging social dining initiatives—such as community meal programs or communal dining events—organizations can play a vital role in reversing the trend of solitary eating and promoting social well-being. This could lead to a more profound societal impact, fostering connections that significantly enhance happiness and mental health outcomes.
Meal Sharing Benefits: A Pathway to Improved Happiness
The benefits of meal sharing extend well beyond mere nutrition; it serves as a foundational pillar for social interaction and overall happiness enhancement. Research underscores that people who engage in regular shared dining experiences report higher levels of satisfaction with their lives and typically experience a greater depth of positive emotional expression. The simple act of gathering around a table creates opportunities for connection that contribute significantly to one’s emotional and psychological well-being.
In light of the growing understanding of meal sharing as a critical component of happiness, communities are now recognizing the value of creating spaces and events dedicated to shared meals. These gatherings not only combat social isolation but also ripple out into broader societal benefits, fostering a culture of connection that helps mitigate the negative mental health impacts often associated with loneliness.
Bridging the Gap: Meals, Happiness, and Policy Interventions
The research pointing to the strong correlation between shared meals and enhanced happiness serves as a significant advocacy for policy intervention. Policymakers can harness this insight to develop programs aimed at fostering shared dining experiences within communities. Such initiatives could be particularly transformative in urban areas where social isolation is prevalent, thereby creating environments that nurture interpersonal connections.
In pursuing these initiatives, it’s crucial to involve local organizations, schools, and businesses, building a framework that encourages and supports communal dining experiences. Through these efforts, we may pave the way to not only improve individual happiness but also restore the importance of community and social ties that have increasingly diminished in modern society.
The Role of Social Connections in Enhancing Well-Being
Social connections play a pivotal role in enhancing individual well-being and happiness. Engaging in shared meals fosters interaction, cultivates empathy, and builds relationships that are essential to mental health. The joy derived from sharing food is often intertwined with celebrating milestones, sharing stories, and establishing bonds that can lead to lasting friendships. Consequently, prioritizing social connections can significantly influence one’s quality of life.
Communities that support opportunities for shared meals can create environments rich in social interaction. This could take the form of community kitchens, potluck dinners, or cultural festivals focused on food, all of which provide avenues for individuals to connect and bond over shared culinary experiences. Such initiatives can effectively bolster social cohesion and contribute to enhanced overall happiness in the community.
Cultural Implications of Meal Sharing and Social Well-Being
Meal sharing is not only a practice that enhances individual happiness but also reflects cultural values around community and belonging. Different cultures emphasize the importance of shared meals as central to their identity, often associating them with family gatherings, celebrations, and rituals. Understanding these cultural implications is vital as they inform how communities can engage in practices that support social well-being.
By celebrating and promoting diverse culinary traditions that inspire meal sharing, communities can create inclusion and interconnectedness among different cultural groups. Encouraging diverse meal sharing practices can foster respect and understanding, enhancing social bonds that contribute positively to collective well-being and happiness.
Looking Ahead: Future Research on Meals and Happiness
Looking forward, future research into the nexus of meals and happiness is critical for better understanding how social interactions during dining can be optimized to improve well-being. Questions such as whether the frequency of shared meals can be linked causally to increases in life satisfaction or are merely linked through social predispositions are essential to answer. Such research could provide valuable insights into the dynamics of social connections.
Additionally, exploring methods to effectively encourage individuals to share more meals could inform targeted public health campaigns. By integrating findings from social science into public policy, communities can take proactive steps to address the mental health crisis highlighted in many regions, using shared meals as a foundational tool for healing and connection.
Frequently Asked Questions
How does dining with others relate to happiness indicators?
Dining with others significantly contributes to happiness indicators. Studies have shown a strong correlation between shared meals and increased life satisfaction. When individuals eat together, they not only enjoy the food but also nurture social connections, leading to enhanced emotional well-being and positive feelings.
What are the meal sharing benefits related to happiness?
The benefits of meal sharing extend beyond nutrition; they foster community and social cohesiveness, which are crucial for happiness. People who regularly share meals report greater satisfaction with their lives, improved mental health, and a sense of belonging that enhances social well-being.
What does the American Time Use Survey say about dining and happiness?
According to the American Time Use Survey, a growing number of Americans are dining alone, which negatively impacts overall well-being. This trend suggests that fewer shared meals might contribute to decreased happiness, highlighting the importance of social interaction during meals.
Can shared meals impact social well-being?
Yes, shared meals can greatly impact social well-being. They provide opportunities for bonding and meaningful interactions, which are integral to building and maintaining relationships. Engaging in these social practices enhances feelings of happiness and community.
Is there a link between meal sharing and happiness research?
Research has established a clear link between meal sharing and levels of happiness. By analyzing data from multiple studies, including the World Happiness Report, it appears that those who eat with others tend to have higher reports of positive emotions and life satisfaction.
Do happy people tend to share more meals?
While studies suggest a strong correlation between happiness and the number of shared meals, it remains unclear whether sharing meals causes happiness or if happy individuals are more likely to engage in meal sharing. Further research is needed to clarify this relationship.
How can increasing shared meals improve community happiness?
Increasing shared meals can bolster community happiness by fostering social bonds and reducing feelings of isolation. Policymakers can encourage communal dining experiences, which in turn may lead to improved overall well-being among community members.
Why are subjective measures of happiness complicated compared to shared meals?
Subjective measures of happiness, such as self-reported happiness scales, can vary significantly between individuals, making them difficult to quantify. In contrast, the act of sharing meals provides a clear, objective indicator that can consistently correlate with well-being.
What role do researchers believe shared meals play in future happiness studies?
Researchers, like those from Harvard Kennedy School, believe shared meals will play an increasingly important role in future happiness studies as an objective measure of social connection and well-being, providing clearer insights into the factors that contribute to happiness.
How can we encourage meal sharing to enhance happiness?
To encourage meal sharing, communities can organize regular dining events, promote family meals, and create public spaces that invite people to gather and share food. These initiatives can help alleviate social isolation and promote happiness within communities.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Shared Meals and Happiness | Research indicates that sharing meals is a strong predictor of happiness, comparable to income. |
| Increasing Isolation | A significant portion of Americans are dining alone, with a 53% increase in solitary meals since 2003. |
| Causation vs Correlation | The research does not definitively establish whether shared meals lead to happiness or if happy people are more inclined to share meals. |
| Measurement Challenges | Unlike subjective measures of happiness, the frequency of shared meals is an objective metric that can better indicate well-being. |
| Policy Implications | Encouraging shared meals may offer a straightforward path to improving community well-being amid rising mental health issues. |
Summary
Shared meals and happiness are strongly interconnected, as the evidence suggests that the more meals people share, the happier they tend to be. Studies have revealed that the act of dining together can significantly enhance an individual’s well-being, making it arguably more essential than factors like income. In a time where social isolation is becoming increasingly prevalent, fostering environments that encourage shared meals can serve as a simple yet effective strategy to boost collective happiness and connectedness within communities.