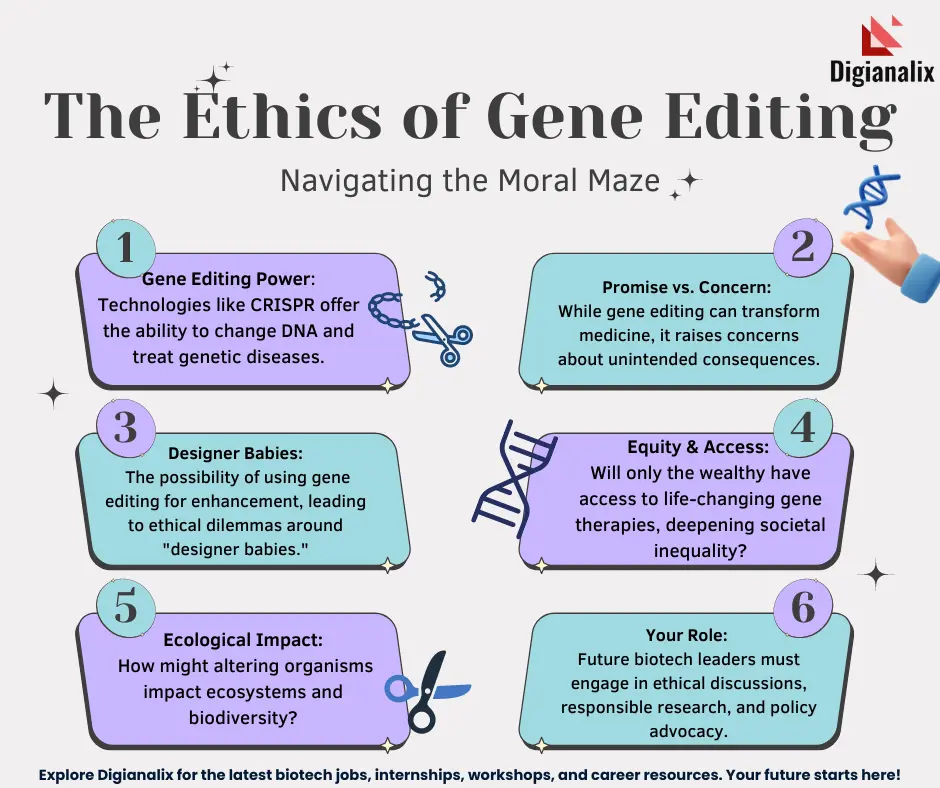
Gene editing ethics is at the forefront of contemporary bioethics discussions, spurred by rapid advancements in technologies like CRISPR. As scientists explore the vast potential of genetic modification to alleviate suffering, such as offering a potential sickle cell cure, the ethical implications become complex and critical. Debates surrounding health equity often arise; who gets access to these revolutionary treatments, and who bears the financial burdens? The promise of gene editing could transform lives, yet it compels us to confront uncomfortable questions about our responsibilities when it comes to altering the human genome. Ultimately, the pursuit of these technologies requires careful consideration of both the intended benefits and the unforeseen consequences they may usher in.
Exploring the moral landscape of genetic alteration, often referred to as gene manipulation or genomic editing, leads us into challenging territory. This evolving field, especially with tools like CRISPR technology, raises significant questions about the appropriateness of modifying hereditary traits or addressing medical conditions. With potential breakthroughs such as the ability to make a sickle cell cure a reality, the discussions shift towards issues of fairness and accessibility in healthcare. As scientists and ethicists engage in bioethics conversations, the implications of genetic innovations prompt us to reevaluate what it means to be human in an age where our biology may be subject to change. Hence, understanding these alternative terms within the context of gene editing ethics enhances our grasp of the complex dynamics shaping the future of medicine.
Understanding CRISPR Technology and Its Potential
CRISPR technology represents a significant breakthrough in the field of genetics, allowing scientists to modify DNA with unprecedented precision. The process involves using a guide RNA to direct the Cas9 enzyme to specific locations in the genome, where it can effectively cut and alter the DNA strands. This mechanism opens up a plethora of possibilities for medical advancements, particularly in treating genetic disorders such as sickle cell anemia. In recent discussions, experts have highlighted CRISPR’s role in potentially curing genetic diseases, showcasing how this powerful tool can change the lives of those affected.
However, the promise of CRISPR is accompanied by substantial concerns regarding its ethical implications. For instance, while editing genes for life-threatening conditions like sickle cell is seen as beneficial, questions arise when considering modifications for traits that merely enhance quality of life. The implications of this technology necessitate a careful examination of the responsibilities that come with such capabilities, pushing us to ask: when does gene editing serve humanity, and when does it cross ethical boundaries?
Gene Editing Ethics: Balancing Innovation and Responsibility
The ethical quandaries surrounding gene editing are as complex as the technology itself. Prominent discussions focus on the moral obligations of scientists and medical practitioners when implementing gene modifications. For example, while some advocate for using CRISPR to eliminate debilitating diseases, others question whether it is right to modify traits like intelligence or physical ability. This delicate balancing act becomes crucial, especially in light of health equity concerns. As noted in recent dialogues, innovations tend to widen the gap between those who can afford cutting-edge treatments and those who cannot.
Moreover, these discussions on bioethics and gene editing are not confined to academic circles; they permeate public discourse, appealing to a broader audience. The narratives around CRISPR have important implications, as they affect how society views health, illness, and the potential for human enhancement. As we delve into bioethics discussions, it is imperative to emphasize that the actions we take today regarding genetic modification will shape the future of healthcare and social justice.
The Impacts of CRISPR on Sickle Cell Disease Treatment
Sickle cell disease has long been a life-altering and often debilitating condition, with traditional treatments falling short of providing lasting relief. The advent of CRISPR technology offers new hope for patients through the potential to correct the genetic mutations causing the disease. Early trials indicate promising results, suggesting that gene editing could transform the lives of those affected by extracting their bone marrow cells, editing them, and reintroducing them into the body to produce healthy blood cells. This paradigm shift in treatment could illustrate the powerful capabilities of precise genetic modification.
However, while immediate results are encouraging, questions remain about long-term effects and broader implications. As treatment costs soar to around $2.2 million, it raises concerns about accessibility and health equity. Will this groundbreaking innovation be reserved for the wealthy, or can equitable solutions be found? These inquiries underscore the importance of considering not just the science behind CRISPR, but also the socio-economic landscape that shapes access to advanced healthcare.
Health Equity and Access to Gene Editing Technologies
Health equity is a pressing concern in the advent of gene editing technologies, particularly CRISPR. As treatments become available, the disparity in access between different socio-economic groups threatens to widen. The high costs associated with innovative therapies, such as those targeting sickle cell disease, suggest that these advancements may not be reachable for many individuals in underserved communities. The implications of this divide call for policymakers and health advocates to consider ways to ensure that all patients have access to cutting-edge treatments, regardless of their background.
Additionally, discussions about health equity should also encompass the need for a more inclusive dialogue surrounding genetic modification. Public awareness and understanding of these revolutionary technologies are essential in advocating for equitable healthcare. By engaging diverse communities in considerations about the future of gene editing, we can collectively work towards a model that promotes not just innovation but also justice in health outcomes.
The Risks of Unintended Consequences in Gene Editing
With the capabilities of CRISPR come considerable risks, particularly concerning unintended consequences of genetic modifications. Although editing a gene may provide a solution for one health issue, it could simultaneously disrupt other essential biological processes. For example, recent advances show promise in lowering LDL cholesterol levels, a positive adjustment for heart health. However, researchers caution that altering genes so intricately tied to bodily functions can lead to unforeseen complications affecting overall health, including insulin regulation and metabolic balance.
This highlights the need for rigorous research and monitoring as we implement gene editing technology. While the potential benefits of CRISPR are monumental, scientists and ethicists alike stress that we must proceed with caution. Comprehensive understanding and thorough investigation into long-term impacts will help mitigate risks and ensure that advancements in genetic modification enhance health outcomes without creating new health crises.
Oversight and Regulation in Gene Editing Practices
The rapid development and application of CRISPR technologies have outpaced existing regulatory frameworks, leaving many policymakers grappling with how to effectively oversee its use. Concerns about misuse, particularly in less regulated environments, raise significant alarm. Instances of genetic modification in countries without stringent guidelines, such as unauthorized germline editing, underscore the critical need for robust oversight. As the science advances, so too must ethical and regulatory structures that govern its application.
Moreover, the issue of oversight extends beyond immediate health consequences. It also encompasses broader societal implications, including the potential for bioweaponization or creating genetically modified organisms with unintended ecological side effects. Therefore, fostering international cooperation among governments and scientific communities is vital to establish comprehensive guidelines and safeguard against potential abuses of this technology.
Public Perception of Genetic Modification
Public perception of genetic modification technologies like CRISPR varies widely, influenced by cultural, social, and ethical perspectives. For many, genetic editing elicits hope for cures to devastating diseases, while for others, it raises concerns about ‘playing God’ or altering fundamental aspects of human existence. This dichotomy represents a significant challenge for scientists and bioethicists in communicating the benefits and possible consequences of gene editing. Engaging with the public to demystify CRISPR and articulate its implications is crucial in shaping a responsible narrative around its use.
Furthermore, fostering a dialogue that includes diverse voices can lead to more informed public opinions, potentially increasing acceptance of genetic technologies. Educational programs and community discussions can empower individuals to express their views and concerns about gene editing, promoting a much-needed exchange of ideas that can inform future regulations and practices, ensuring that advancements align with societal values.
The Future of Gene Editing in Medicine
The future of gene editing in medicine appears promising, with ongoing research and clinical trials paving the way for new therapies that could revolutionize treatments for various genetic conditions. The potential to eradicate hereditary diseases like cystic fibrosis and muscular dystrophy through targeted modifications signifies a shift in how we approach genetic disorders. As technology continues to evolve, we can expect to see more innovative applications of CRISPR that go beyond traditional boundaries of medical treatment.
However, as we look ahead, it is essential to balance scientific progress with ethical considerations and equitable access to new therapies. Ensuring that the benefits of gene editing are shared across all demographics remains a priority. The conversation must evolve from solely a focus on technological capability to include comprehensive discussions about societal impact, responsibility, and the potential for health equity in the ever-expanding field of genetic modification.
Ethical Dilemmas of Genetic Enhancement
As CRISPR technology opens the door to genetic enhancement, it also ignites profound ethical dilemmas about the extent of human intervention in natural processes. The possibility of designing traits such as physical appearance, intelligence levels, or even personality raises significant philosophical questions. Discussions around whether parents should have the authority to decide on such adjustments for their children, or the potential societal pressure to conform to genetically modified standards, feature prominently in current bioethics debates.
Moreover, the implications of genetic enhancement extend beyond individual families. If the ability to modify traits becomes normalized, we may face societal divides based on genetic modifications, fostering a new dimension of inequality. Engaging in ethical discussions surrounding genetic enhancement is therefore vital in shaping a future that respects individual autonomy while considering the collective ramifications of such profound choices.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the ethical implications of using CRISPR technology in gene editing?
The ethical implications of using CRISPR technology in gene editing are multifaceted, involving questions of consent, equity, and societal impact. As gene editing can potentially eliminate diseases like sickle cell anemia, it raises concerns about who decides which traits to modify, the cost of treatment access, and the risk of exacerbating health disparities. Bioethics discussions focus on ensuring that advancements benefit all, not just a privileged few.
How does gene editing relate to health equity, especially in the context of CRISPR?
Gene editing through CRISPR technology poses significant health equity challenges. While it offers the potential to cure genetic disorders, such as sickle cell anemia, the high cost of treatments (estimated at $2.2 million per patient) raises questions about accessibility. Health equity must be prioritized to ensure that all populations, particularly marginalized groups, can benefit from gene editing advancements.
What are some ethical concerns about editing germline genes with CRISPR?
Editing germline genes with CRISPR raises ethical concerns regarding future generations, consent, and potential misuse. These changes affect not only the individual but also their descendants, leading to debates about the appropriateness of such modifications for non-life-threatening conditions, holistically examining the ramifications of ‘designing’ future children and the implications for human diversity.
What role do bioethics discussions play in advancing gene editing technology?
Bioethics discussions are crucial in advancing gene editing technology, particularly in assessing the societal and moral implications of actions like CRISPR gene editing. They promote critical dialogue about consent, equity, and what constitutes responsible use, ensuring that innovations serve the broad public interest and adhere to ethical standards.
How might gene editing impact the concept of human variation and diversity?
Gene editing, especially through technologies like CRISPR, could impact the concept of human variation and diversity by enabling the modification of traits traditionally viewed as variations, such as deafness or other genetic conditions. This raises pivotal ethical questions about whether such modifications are necessary or desirable and emphasizes the value of recognizing human differences as part of our collective humanity.
What are the risks associated with unintended consequences from gene editing?
The risks associated with unintended consequences from gene editing are significant, as genetic modifications can disrupt complex gene interactions. For example, while lowering LDL cholesterol may seem beneficial, it could affect other metabolic processes. This highlights the need for thorough evaluation of gene editing outcomes to avoid harmful repercussions and ensure safe application.
Who should be responsible for regulating CRISPR gene editing practices?
Regulating CRISPR gene editing practices is a shared responsibility that involves governments, regulatory bodies, and the scientific community. As advancements are made, there’s a pressing need for robust oversight to prevent unethical practices and exploitation, particularly in regions with lax regulations, ensuring compliance with global bioethical standards.
Can gene editing using CRISPR exacerbate health disparities?
Yes, gene editing using CRISPR has the potential to exacerbate health disparities if access to treatments is unequal. As the technology becomes available, the cost and availability of gene therapies could lead to a divide between those who can afford them and those who cannot, thus widening the gap in health equity.
What are the moral dilemmas of modifying traits in children using gene editing?
Modifying traits in children using gene editing presents moral dilemmas, particularly regarding parental authority and the rights of the child. Decisions to edit traits for aesthetic or non-medical reasons challenge our understanding of consent and the implications of ‘designing’ children, necessitating careful ethical consideration and societal dialogue.
How do technological advancements in gene editing impact society’s view of disabilities?
Technological advancements in gene editing may shift societal views of disabilities, as they introduce the possibility of ‘curing’ conditions previously accepted as part of human diversity. This raises ethical questions about acceptance, the value of different abilities, and the implications of viewing disabilities through a pathological lens rather than a spectrum of human variation.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Ethical Dilemma | Is it right to change human differences? Should we use CRISPR to alter conditions like Down syndrome? |
| Medical Advances | CRISPR offers potential cures for genetic diseases like sickle cell anemia but raises questions about who should decide on such interventions. |
| Cost and Access | The treatment for sickle cell is around $2.2 million, leading to concerns about health equity and affordability. |
| Parental Decision-making | Should parents be allowed to make genetic modifications for their children regarding desirable traits? |
| Oversight Issues | Who regulates gene editing, particularly in countries with less strict guidelines? |
| Unintended Consequences | Gene editing can lead to unforeseen effects since genes interact within complex biological networks. |
Summary
Gene editing ethics is a complex topic that intertwines medical advancements with profound moral questions. As gene-editing technologies like CRISPR develop, we confront the ethical implications of altering human genetics. The promise of curing genetic diseases comes with considerations of equity, parental rights, oversight, and the importance of human diversity. It is crucial to navigate these ethical waters carefully, as the impact of gene editing will shape the future of medicine and society.